La Transclase volvió a salir. Esta fue nuestra visita y trabajo intensivo…más o menos.. Gracias a los compañeros que nos recibieron e invitaron.
John Vandermeer discutiendo el 6to mito
Así como nosotros en la Transclase, John lo había hecho hace unos años…
THE SIXTH DEVELOPMENTALIST MYTH OF AGRICULTURE (FROM LEWONTIN AND LEVINS, “BIOLOGY UNDER THE INFLUENCE”) AND COMMENTS ON ITS RESOLUTION
In their chapter “Seven developmental myths about agriculture”, Levins and Lewontin talk specifically about specialists and generalists and assumptions that seem to drive ever increasing specialization, in their 6th myth. I here quote that myth and then add some comments that I think could be relevant to modern food systems (and other subjects too).
“Specialists are modern, generalists backward. The rational kernel in this view is that there is too much to know within every discipline for anyone to know everything. The history of European thought has been an increasing subdivision of knowledge from the days of the philosopher-scholar-theologian, through general “scientists,” to the present multiplication of specialties within previously coherent fields of study. For example, genetics, a part of biology, now includes molecular genetics, cytogenetics, population genetics, quantitative genetics (for plant and animal breeding), as well as further breakdowns by kinds of organisms studied. Developing countries speak with pride of the numbers of specialists who graduate from their schools. Uncritical admirers of specialization propose that groups of specialists working as teams can solve problems related to the subdivision of knowledge within a field. However, specialization prevents the researchers from seeing the whole picture, both because of the narrowness of their training and because the ideology of expertise makes it a matter of pride to consider only precise quantitative information as real science while the rest is “philosophy” (a bad word among positivistic scientists) or “not my department.” The training of specialists rather than the education of scientists encourages the combination of micro-creativity and docility that permits scientists to work on the most monstrous projects of destruction without attention to their consequences. The great failings in the application of science to human well-being have come about not because of the failure to examine the system in its complexity. The strategy of the Green Revolution is solving many and difficult technical problems of plant breeding, but the geneticists did not anticipate problems of pest ecology, land tenure, or political economy, and as a result increases in production are sometimes associated with increases in misery. The Aswan Dam was an engineering success in that it retained the water it was intended to retain. But by stopping the seasonal flooding that provided renewed soil fertility, the dam made farmers dependent on imported chemical fertilizers; the reduced flow of water into the Mediterranean Sea increased salinity and adversely affected fisheries; the outflow of the Nile was reduced to the point that it could no longer offset the erosion of the coastline; the irrigation ditches became the habitat for snails that transmit liver flukes.
It is a common experience that in large programs of development the ministries of health and agriculture do not talk to each other; thus it come as a surprise when the expansion of cotton production increases malaria. Cotton is very heavily sprayed. The natural enemies of the mosquitoes are killed, allowing the mosquitoes that transmit malaria to thrive in habitats created for them by the clearing of forest. The immigration of a labor force not previously adapted to malaria allows the parasites ideal susceptible hosts. There is a vast oral tradition of such cautionary tales. The point is that most of these “unexpected” outcomes are predictable, at least in principle. There is no longer any excuse for planners not to ask the obvious questions about a program, such as: what will it do to the position of women? New technologies are usually handed over to men, and traditional women’s occupations are displaced. For instance, the use of herbicides displaces women from weeding. How will vegetational changes alter the biology of potential disease vectors? Will the new productive activity be compatible with the water needs of the people? Will the production of export crops make the food supply more vulnerable?
The outcome of short-sighted specialization is that each department takes as its starting point the products of the department next door. Crops are bread for their performance in monoculture because the machinery was designed for operations in pure stands of a single crop. The engineers design machinery for monoculture because the agronomists inform them that it can replicate what farmers do. The farmers plant monocultures because their varieties and machinery are suitable to monoculture. Each party is making rational decisions given the constraints imposed by the others, giving the whole trajectory of technological development the appearance of inevitability and necessity, while nobody looks out for the process as a whole.”
Resolving the 6th: The move towards interdisciplinarity, promoted as a goal in US universities for the past 10 years, is an implicit acknowledgement that what L and L say here is correct, yet the university’s response is lame. Embarrassingly, the group of scholars with whom I affiliate seems to mimic the lame approach of the university. In planning a project it is normal, and thought to be wise, to seek out experts from across a broad intellectual spectrum. While it is difficult to criticize such an approach, it is in the end an intellectually lazy approach. Interdisciplinarity is, in and of itself, an intellectual challenge that is only dodged by assembling a team of experts. Indeed, historically we see the emergence of great creativity when disciplines are merged and then deepened, rather than deepened and then merged. When biochemistry emerged as an independent science it was not because of a university program that encouraged chemists and biologists to talk to one another. It emerged out of independent scholars asking questions at the interface of those two classical disciplines. The department of Women’s Studies is clearly an amalgam of sociology, literature, psychology, and many other mainly social science disciplines, and emerged from independent scholars asking questions, unified by an interest in issues specifically attached to gender, at the boarders of their traditional disciplines. Similar narratives can be easily constructed for Biophysics, African American studies, American Culture, Complex Systems, and many others.
In contrast, the continual splitting of intellectual disciplines is the other dynamic component of intellectual phylogenies. We now have two biology departments (Cell and Molecular and Developmental Biology (MCDB) and Ecology and Evolutionary Biology (EEB)), but that split was of a department that had originally been a merger of two others (Zoology and Botany). I have been here long enough to watch both the merger and split, and I would not be at all surprised to see further splits and mergers as both knowledge increases and as petty intellectual territoriality evolves (splits frequently happen because faculty are sometimes like kids in a sandbox).
Since all intellectual activity is located in metaphor and simile, in thinking about the problem of interdisciplinarity, we need an appropriate metaphor. A lake has depth and superficial extent, pretty good potential metaphors. There are those who have extremely broad knowledge (Jack of all Trades,, etc. . . ), covering the entire surface of the lake, and there are those who have very deep knowledge, extending to the depths of the lake, but only within a narrow section. For those (like me) who appreciate a graphic, figure 1 is useful for further discussion.
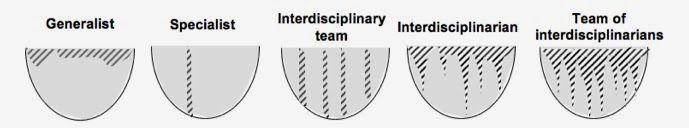
Figure 1. A metaphorical lake basin containing all “truth” about a subject (the shaded area) and the various pieces of “knowledge” we have of that truth (hatched area).
Both generalist and specialist knowledge is legitimate, to be sure, but, like all knowledge it is incomplete. What is special about the incompleteness is its fixed nature. If the specialist understands his and her limits, and, true to the specialist ideology, is forbidden to transcend those limits, it is almost inevitable that interdisciplinary teams will fail to cover much of the “truth space” with “knowledge.” The interdisciplinarian, although less broad than the generalist and less deep than the specialist, combines disciplines so as to sometimes take note of critical overlaps in the knowledge space. And, evidently, the team of interdisciplinarians, with such overlaps continually exposed and, hopefully, acknowledged and pursued will eventually cover the truth space with knowledge, perhaps quicker and with greater efficiency.
En honor a Richard Levins
BRANCHING PATHWAYS OF DEVELOPMENT
Presentation to the symposium “Sustainability in the Balance” at Tufts University School of Nutrition April 11, 2006
Richard Levin,Harvard School of Public Health , Boston, Massachusetts, USA and Cuban Institute of Ecology and Systematics, Boyeros, Ciudad Havana, Cuba
«Agriculture is one aspect of the crisis. Simply stated, people are hungry and world capacity to produce is being undermined, but the undermining is covered up by dumping in more fertilizers and chemicals and expanding horizontally into less and less suitable areas. Consider for a moment the simple fact of hunger. Is it that they are doing their best but their best isn’t enough? But in that case how come farmers are being forced to abandon farming? How come coffee, tea, and drugs dominate the world trade in agricultural products? How come crops are often grown in unsuitable habitats or that wheat production was increased in India at the expense of chickpeas? Why does Mexico import corn? How come precious water in Rajistan is used to grow chili peppers, lowering the water table, and the Sahel exported fresh flowers to Europe during the drought of the 1970’s? Or maybe science doesn’t understand enough to produce sufficient food? But in that case why does so much research go into marketing or inventing marketable commodities to sell farmers as inputs, and so little into finding gentler technologies?
But if we consider an alternative hypothesis it begins to make sense: agriculture is not in the business of feeding people but of producing marketable commodities. The distinction between commodities and utilities is fundamental to our understanding of the dynamics of capitalism»
Ejemplo de reporte de lectura
Necesidades
Iván Illich
Tesis central de autor: La condición humana ha llegado a ser definida por la necesidades comunes a todos sus miembros. Las necesidades substituyen valores culturales, sociales y políticos en cada lugar donde se reproducen y por lo tanto implica necesariamente mecanismos de violencia para su implantación
Desarrollo de la idea: La necesidad como condición prioritaria en el ser humano y como búsqueda objetiva en la sociedad. El homo sapiens pasó a ser el homo miserabilis cuando las necesidades básicas invadieron la mente y los sentidos y se constituyeron como sinónimo de deseo alcanzable. Los hábitos de necesitar se han establecido por el discurso del desarrollo.
No puedo hacer otra cosa más que citar:
“Y la mayor parte de estos cinco mil millones actualmente vivos aceptan sin cuestionamiento su condición humana como dependiente de bienes y servicios, dependencia que ellos llaman necesidad. En justamente una generación, el hombre necesitado –homo miserabilis– se ha convertido en la norma.”
Los servicios que se piensan “básicos” se instauran como necesidad de la población y a su paso forjan anhelos y querencias en la gente que no cuenta con ellos. Bajo esta concepción desaparecen las carencias y no hay limitaciones para las gente, lo único que hay son necesidades, muchas veces no cumplidas. Resumidas por Illich en el “todavía no”.
Las necesidades resultan el pilar con el cual trabaja el desarrollo, está claro cuáles son, está claro que las tenemos que alcanzar, el único problema es cómo le vamos hacer para llegar a satisfacerlas. El desarrollo ofrece la confianza del progreso material y social y el crecimiento económico. En este sentido la pobreza, se entiende como una medida de la carencia personal en cuanto a los servicios y artículos necesitados.
Las necesidades son reconocidas ontológicamente y todo mundo tiene que satisfacerlas, es parte de los requerimientos sistémicos de todo ser humano, en este paso el humano se convierte en cyborg y pierde todo el trasfondo cultural que lo reproduce como humano social.
¿Qué opino? Discusión
Me rompió todo el esquema de economía no monetaria que se basa en las necesidades. Llegamos a pensar que las necesidades a cumplir son meramente materiales. Puede ser que el concepto de necesidades se amplíe si lo definimos en torno a las necesiades básicas y añadimos distintos objetivos como necesidades de recreación, políticas, amorosas, de asociación, de expresión y de producción. Entonces nos alejamos de una definición material, pero el mismo concepto no va más allá ni puede deshacerse de la crítica certera que le hace Illich, la necesidad se vuelve inherente al ser humano y si no la satisface deja de ser. Esto obliga a que siempre haya que definir la necesidad y regresar a tratar al ser humano como un cyborg.
Conclusión ¿qué preguntas me genera?
¿Qué es lo inherente al ser humano?¿qué lo distingue de todos los demás seres vivos? La necesidad no. Habría que buscar otro concepto para definir economía si queremos pensar que otro mundo es posible.
Transclase…
Este espacio que se ha generado como una materia optativa de la carrera de Biología en la Facultad de Ciencias de la UNAM es una apuesta, no es algo que está definido y decimos que está en constante construcción.
La invitación apunta a que los estudiantes y profesores más allá de su identidad en el aula se reconozcan como personas con posibilidades de construir objetivos y proyectos concretos que tengan un compromiso social y una práctica concreta.
La clase pretende salir de las aulas, invitar siempre, sacar la reflexión, discutir y dialogar con otros y tratar de crear espacios de formación que no se restrinjan a la Universidad. Queremos que la universidad vuelva a la gente con un sentido y compromiso desde la agroecología.
Una clase para pensar sobre la autogestión académica y sus posibilidades de vinculación con experiencias y esfuerzos organizativos.
El corazón de la transclase son los estudiantes que son los que van a mantener y a nutrir el esfuerzo. Al mismo tiempo que es su espacio es un espacio brindado a otros, comprometido con otros.
El espacio no será un cooptador de conciencias, o va imponer una ideología o marcará el rumbo, ese se irá construyendo colectivamente.






























Debe estar conectado para enviar un comentario.